By the time you’re finished reading this article your weed knowledge will go from “grandma” to “Snoop Dogg”.
I think you’ll agree with me when I say that cannabis culture can be confusing at first. You’ve probably seen it yourself — there are hundreds of different products and consumption methods, which makes it hard to find a good place to start.
As a beginner, it’s crucial that you know the basics. Which is why we prepared the most in-depth guide to cannabis on the Internet.
After reading this guide, you will be able to impress your friends with the following:
- How weed was used through history
- What are THC and CBD and what do they do
- What are cannabis strains and how to pick the right strain for you
- How to roll a joint and use a bong
- How is the plant grown from seed to dried bud
- And much, much more
But it’s not all about impressing your friends. The biggest reason you need this guide:
Make more educated decisions.
In the end, it’s all about what you use and how you use it. For example, if you decide to purchase an ounce of dried flowers, you should know which strain is the best for daytime use and which for night. You might also want to know how to roll a joint or how to get started with growing your own cannabis.
And as you know, every journey begins with the first step.
So let’s jump right in.
Contents
- History of cannabis
- Anatomy and chemistry of the plant
- Guide to cannabis strains
- Commercial cannabis products
- Cannabis consumption 101
- Cannabis growing & production
Chapter 1
History of Weed
If there was just one sentence that could explain this chapter, then it would have to be:
Cannabis has been used by humans for over 12 thousand years.
Over the course of those 12,000 years, the plant spread from the steppes of Asia to North America, touching almost every area of the world.
Cannabis originated in Central Asia, where it was soon discovered by nearby populations and spread to China. It was in China where it reached its full potential as a cultivated crop.
From there it spread to Korea, India and finally got into the hands of Scythians — Indo-European nomads who brought the seeds to Europe.
Cannabis then, being a highly adaptive plant, traveled its way through Europe and into Spain. Over the course of several thousand years, the plant also made its way to Africa and into South America.
In the 1800s the plant reached South America and in 1900s migrated to North America, which was its final stage of spreading out over the globe.
By now, you’re probably wondering why cannabis was used by ancient civilizations.
Archeological finds support the claim that our ancestors were familiar with hemp’s possibilities early on, which can be seen in the fact that they started cultivating it around 10,000 BC.
China led the way in cultivation and, at around 6,000 BC, some of their province’s economies were massively influenced by cannabis and its produce.
Rope, oils, paper, flowers — you name it, they traded it.
With cultivation came wide application (no rhyme intended).
The first documented use of cannabis as a medicine goes back to 2,737 BC, thanks to emperor Shen Neng of China, who was prescribing marijuana tea for treating rheumatism and gout.

Chinese also used hemp for paper and clothing, next to obvious medicinal and psychoactive purposes. People of India used cannabis for religious ceremonies and pain relief and Egyptians used it for treating sore eyes and cataracts.
It was extensively used by ancient Greeks for treating tapeworms and inflammations and it even got mentioned in one Herodotus’ document.
Once the plant reached Britain, France & western Europe, it became topic of books in the Middle Ages.
Anne of Brittany, Queen of France, commissioned a book of hours in 1508 which contains the first ever botanic depiction of the plant in the western world.

Image source: commons.wikimedia.org
As you can see, marijuana was widely used by a lot of civilizations and it all took a wrong turn when it started being prohibited in the 20th century, right after Mexican Revolution.
As Mexican immigrants poured into the South, USA needed a palpable reason to detain them and reduce immigration.
Seeing how Mexicans constantly used marijuana, the US decided to criminalize the plant and use it as a basis for keeping them in check.
From there on out, criminalization became a valid strategy for keeping a certain population under control and cannabis, unfortunately, took one for the team. But let’s not get into politics here.
The plant remained criminalized for almost 60 years, regardless of the fact that it was extensively used and popularized by liberal society.
The hippie movement contributed a lot to the acceptance of marijuana in the West, even though it remained a banned substance.
In the 1960’s, American youth rekindled cannabis consumption and unintentionally branded it as a fun, social drug that could not be compared to harder, addictive drugs.

Image source: Grass Documentary
In 1976, Netherlands decriminalized cannabis, allowing possession and sale of up to 30 grams. This spun off the creation of coffee shops, one of the main tourist attractions of Amsterdam.
However no one was legalizing the plant yet. That is, until another major milestone in its history.
In 1996, California legalized the use of medicinal cannabis through a law called California Proposition 215.
This was pretty big, because the Proposition 215 was a statewide vote that came through despite the lack of FDA’s approval.
The next big milestone came in 2014, when Colorado allowed selling marijuana for recreational use. This has produced amazing results, bringing the state increased tax revenues and a total of $996 million to the producers during the course of 2016.
Now, there are more than 24 countries that have either legalized or decriminalized weed, which is a tremendous leap forward compared to the early 1900s.
However, Uruguay is leading the pack on a nationwide level, as they have completely legalized sale, possession, transport and cultivation of cannabis in 2013, without any limitations.
Chapter 2
Anatomy and Chemistry of the Plant
Now that we know how cannabis came to our neck of the woods, we can explore its biological and chemical composition. And this is the stuff that makes it so fun.
Knowing this can help you in a lot of areas, but especially when choosing which product to buy and how to assess whether it’ll be good for you or not.
First things first — sexual reproduction.
Cannabis is, in a lot of ways, like a human. It adapts to its environment masterfully, it has a life cycle and it has an important sexual reproduction system.
Cannabis plants can be either male, female or both (hermaphrodites). Since hermaphrodite plants are pretty rare nowadays, we will focus on the boys and girls.
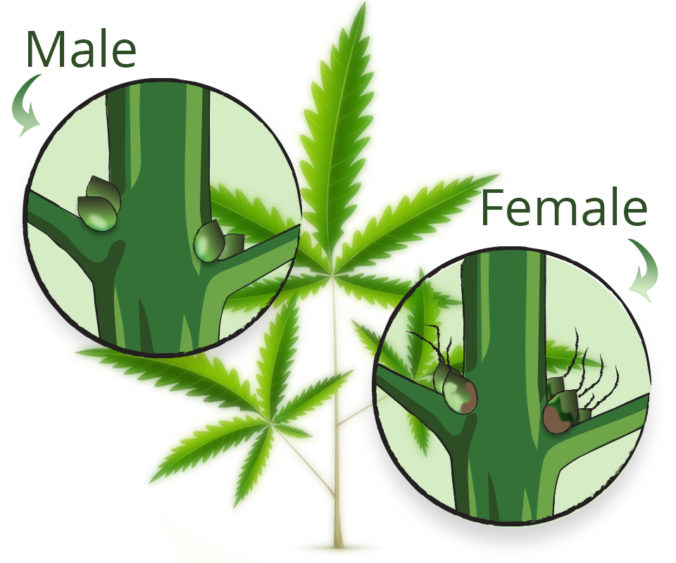
So, here is a rapid-fire explanation of how cannabis would reproduce in the wild
Male plant grows, forms pollen sacks, matures and then releases the pollen. Pollen flies out into the air, gets attached to a female flower, which then develops and sheds seeds. New plants are born, old plants die and the species keep surviving. The end.
However, modern legal cannabis cultivators realized two things:
- Male plants do not have nearly enough cannabinoids (psychoactive and healing compounds) as female plants
- Unpollinated female plants contain an insane amount of cannabinoids (THC and CBD)
Their conclusion — let’s focus on cultivating unfertilized female plants.
Right now, female cannabis plants are the bread and butter of the cannabis industry. Every single cannabis product you buy comes from a female cannabis plant.
So, let’s explore what makes up a female cannabis plant:
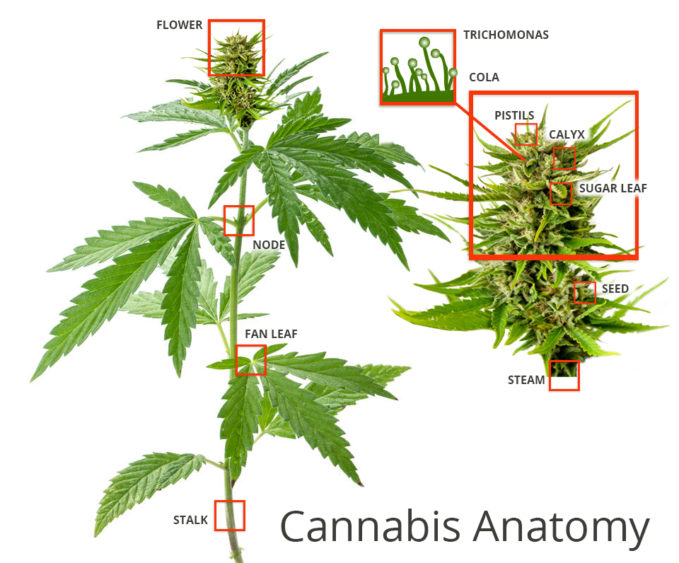
As you can see from the image above, there are 8 important areas you need to know about:
- Stems (stalks)
- Fan leaves
- Colas
- Sugar leaves
- Calyxes
- Pistils
- Trichomes
Stems
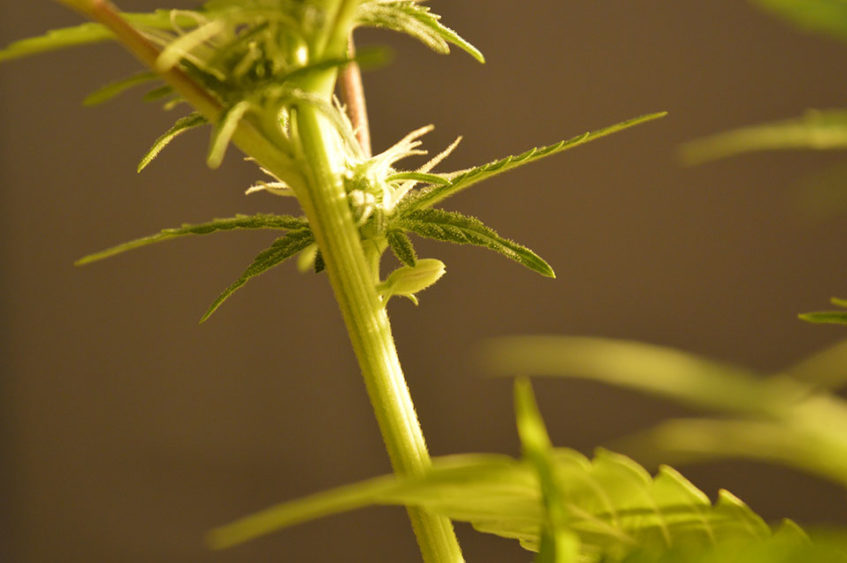

Image source: Cannabis Pictures
Stems represent the main body of the cannabis plant. They are long and thin and they provide support for flowers while delivering important nutrients to them.
Stems are not rich in psychoactive substances, and they are usually used for producing fiber.
Over the years, people came up with lots of alternative uses for their stems, like making tea or weaving hemp baskets.
Fan Leaves
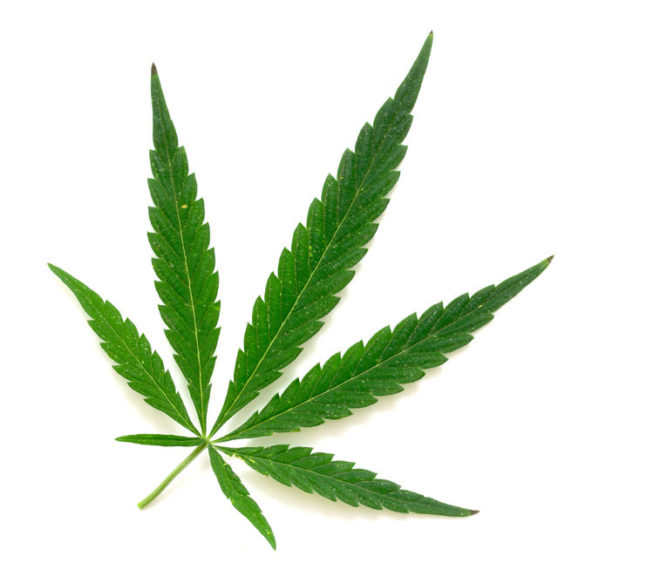

The international symbol of weed is also its primary source of energy. Fan leaf captures sunlight and turns it into life-nurturing fuel.
They are usually not consumed, as they contain only traces of important substances, but they are extremely important for overall plant health.
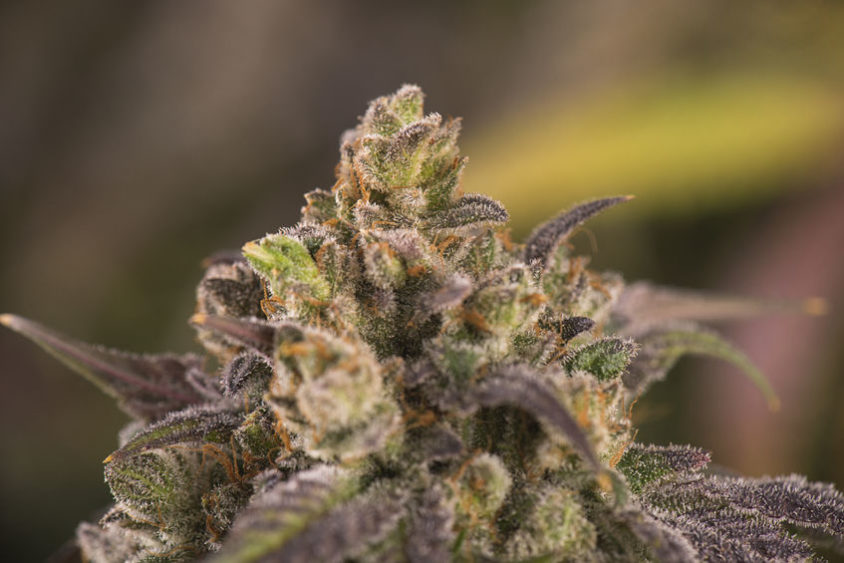
Colas
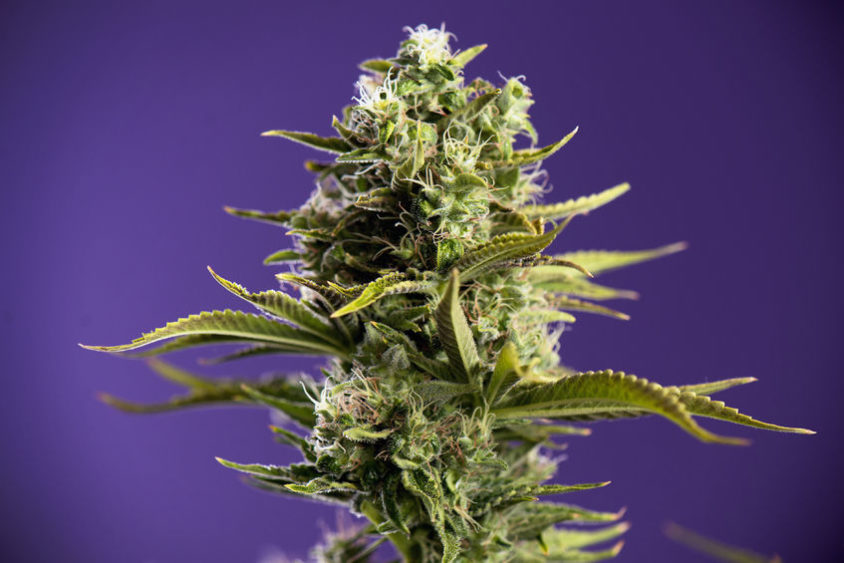

Cola is, simply put, a term used to describe a section of the plant where the flower grows.
The highest flower is usually called the main cola, however other colas can appear on other branches. In the wild, most plants usually grow a single, big cola.
Modern cultivation techniques allow for multiple colas to be grown, which increases the total yield.
Lastly, colas are comprised of calyxes, which are, arguably, the most important parts of the plant for us consumers.
Calyx
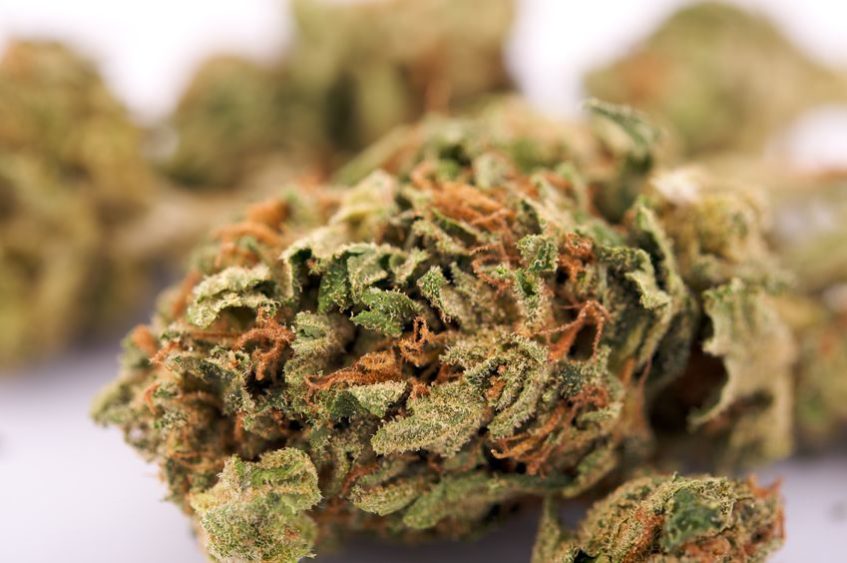

Cola is the section of the plant where flowers grow but calyx is the actual flower.
It is also known as bud or just simply flower. One calyx (or one bud) is made out of sugar leaves, pistils and trichomes, all of which contain cannabinoids and terpenes (medicinal substances and aromatic molecules).
When you buy cannabis flowers, a cola is what you get.
Sugar Leaves
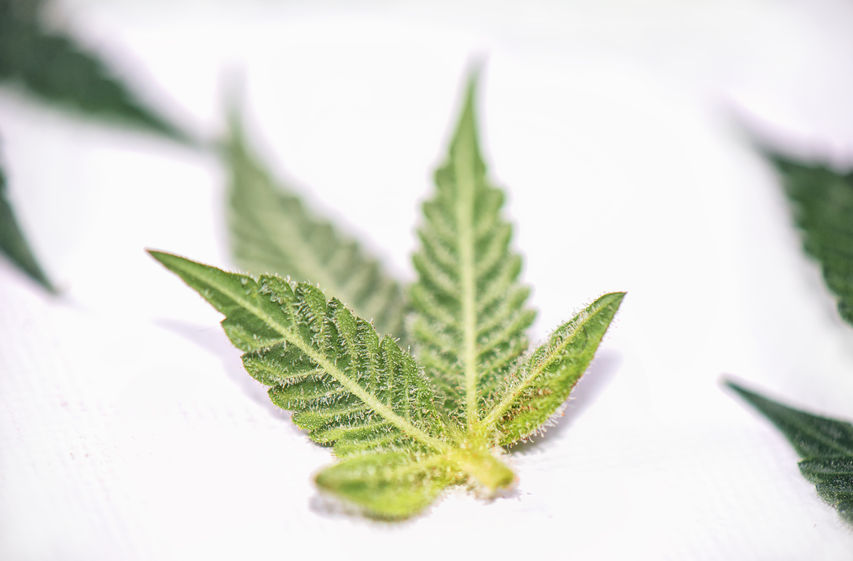

Sugar leaves are “baby” leaves that grow inside the cola. Unlike fan leaves, they are much smaller in size, packed with terpenes and, for that reason, they look like they’ve been sprinkled with sugar.
Naturally, they are extremely high in psychoactive and medicinal substances.
Pistils

Pistils are thin and colorful strips inside the flower. They are the main reproductive organ of a female cannabis plant.
Biologically, their sole purpose is to grab pollen from the air and develop seeds.
Once the pistils start growing, they are usually white or pale in color, and as the plant matures, they change their color, which can be used as a non-accurate method of identifying whether a flower is ready to be harvested.
Trichomes
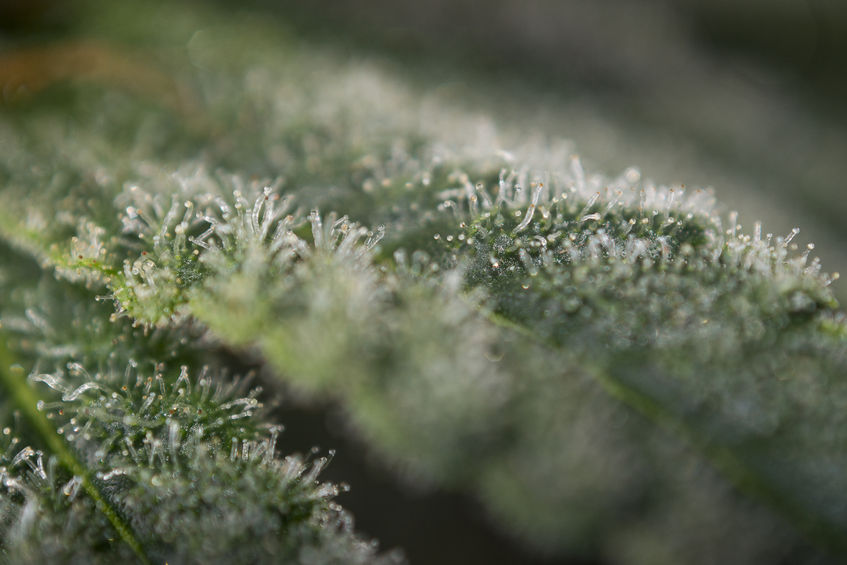

Trichomes are the resin glands that grow on cannabis flowers and leaves and they are, essentially, the main culprit to the plant’s popularity.
Trichomes are translucent, mushroom-like structures on the top and are packed with the good stuff.
It is suspected that these evolved as the plant’s defense system but, right now, you need to know that every bit of a plant’s effects comes from trichomes.
The highest concentration of trichomes is around the actual flower and the nearest sugar leaves, while the fan-leaves remain pretty much trichome-free throughout the plant’s growth.
What are cannabinoids & terpenes?
OK, we recently mentioned cannabinoids & terpenes, so let’s explore them in more detail.
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds that are produced inside the cannabis plant, particularly in trichomes, and they are the substances that produce effects when the plant is consumed.
Once we consume cannabis, these cannabinoids travel through the bloodstream and attach themselves to our very own cannabinoid receptors — CB1 and CB2.
These receptors are a part of our endocannabinoid system (ECS), a system that our body uses for regulating mood, pain, sleep and appetite.
The biggest takeaway:
Cannabinoids are great at putting our ECS system in balance, therefore catering to a wide number of medical users.
On the other hand, cannabinoids serve recreational users as well, by providing them with psychoactive effects.
When a person experiences a high, it is because a cannabinoid called THC latches on to CB1 receptors in the brain, which then kicks off a cellular reaction. The end product is an euphoric feeling that the user experiences.
Terpenes are essential oils that give cannabis its smell and taste. They also contribute to plant’s medical effects by aiding cannabinoids in crossing the brain-blood barrier.
Terpenes also have the ability to increase the activation of CB1 receptors, thus boosting the effects of cannabis.
Taste also plays a big part in the popularity of a strain and you will often encounter taste discussions between users on marijuana forums and review sites.
Terpenes are developed within trichomes (along with cannabinoids). Plants grown organically usually have the most complete terpene profile.
THC and CBD explained
Cannabis has more than 60 different cannabinoids, but we will now cover two compounds that you will encounter the most: THC and CBD.
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) is the only intoxicating cannabinoid and it causes the user to feel its effects by binding into the cannabinoid receptors.
Signature effects of THC are euphoria (or buzz), a slight sense of time distortion, accompanied by happiness, energy, relaxation and many more, depending on the strain.
Due to its interaction with our endocannabinoid system, THC relieves a lot of symptoms for medical users as well.
It has been known to relieve chronic pain, spasms and even nausea.
THC percentages usually vary from 5-20% in dried flowers and up to 95% in concentrated extracts. Since you are a beginner, have in mind the following — the higher the THC percentage, the stronger and more potent that product is (and the stronger your high will be).
CBD (Cannabidiol) is the second most prominent cannabinoid, however, it is a non-psychoactive substance.
CBD has extremely strong anti-inflammatory properties and is generally desirable for medical users who would like to relieve certain symptoms without getting intoxicated.
Being non-psychoactive, CBD is widely used in treating epilepsy, anxiety and even metabolic disorders.
THC and CBD percentages vary for each plant, which has a lot to do with both the strain type as well as how healthy and carefully it is grown.
Lately, there have been more cannabis strains that are CBD dominant, and those have around 8-15% of CBD and 5-10% THC.
As you can see, these two cannabinoids possess plenty of healing properties and are the reason why cannabis has been so successful in treating medical conditions throughout its 12,000 year old history.
Chapter 3
Guide to Cannabis Strains
When learning about cannabis, you will often come across a term strain. The definition of the word strain is “a genetic variants of the same species”.
There are 3 main strains (subspecies) of cannabis: Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica and Cannabis ruderalis.
The fourth type of cannabis is also the most abundant today and it belongs to hybrids of these 3.
Cannabis sativa
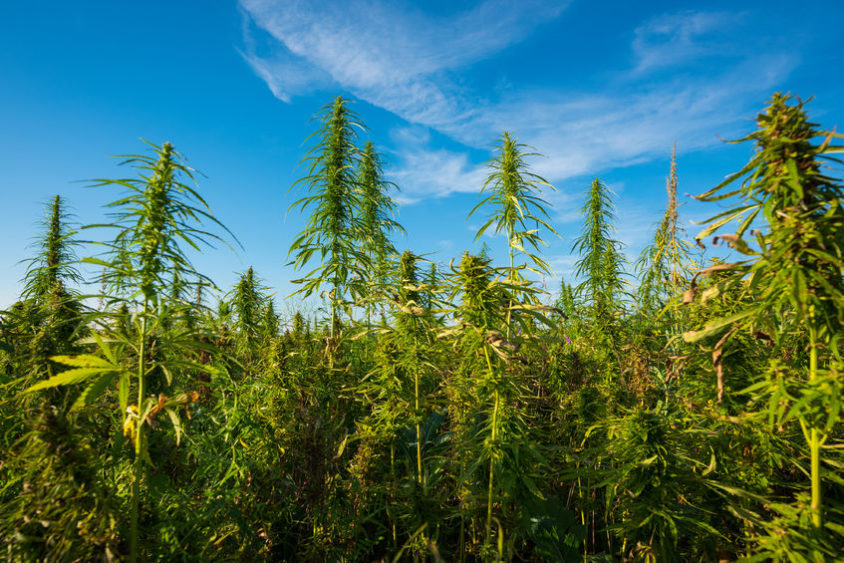

Cannabis sativa is among the most widespread strains. It takes relatively long to mature and is easily recognized by its narrow and tall appearance.
It’s usually 2-4 m tall, less dense and has more elongated buds. Its leaves are light green and the plant has a pleasant (sweet) aroma.
When consumed, cannabis sativa produces euphoria—a feeling that can be described as a cerebral high, causing an influx of energy and creativity.
Cannabis indica
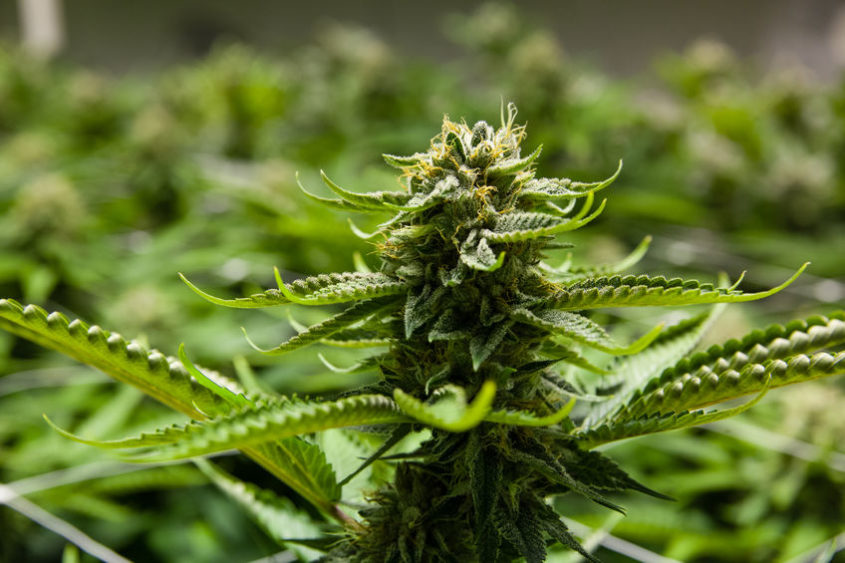

Cannabis indica originated in Afghanistan, Pakistan and India and it is a hugely popular subspecies.
It is characterized by relatively short and stocky appearance, which, interestingly, perfectly adapts to relatively cool regions as well.
As you can see from the image above, Cannabis indica is highly branched, with darker leaves and a sour aroma.
It flowers early, which makes it a popular choice among growers, along with the fact that it’s more compact than sativa—a trait that makes it ideal for grow tents and covert growing.
Due to its high myrcene contents, indica strains usually have a sedative, calming effect, making this species perfect for nighttime use.
Cannabis ruderalis
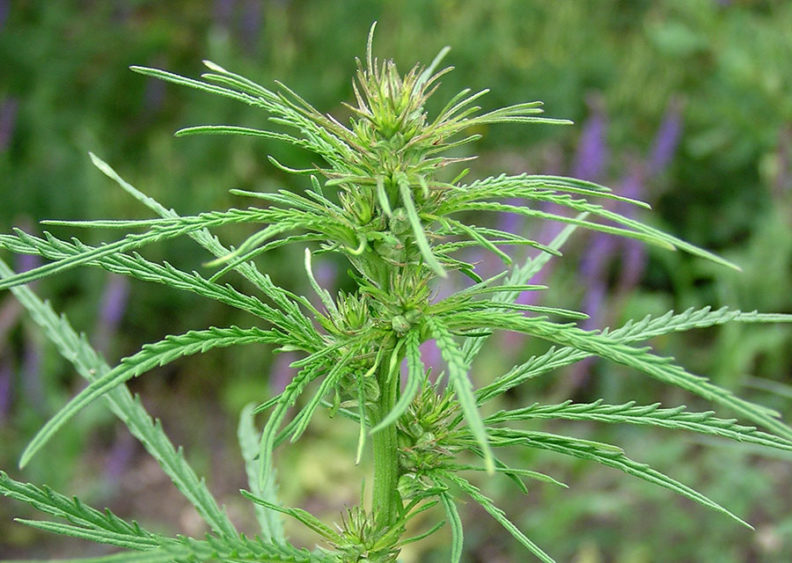

Cannabis Ruderalis is the least known strain, but you may come across some of its hybrids every once in awhile.
As you can see, the plant is quite small, ranging from 30-70 cm in height.
It does not have enough cannabinoids to “make it big” on its own, but it does have one feature that is perfect for cross-breeding (creating hybrid sorts) which is its autoflowering gene.
While Cannabis sativa and indica need to be exposed to light right after sprouting, Cannabis ruderalis species flower on their own after about 3 weeks.
Therefore,this strain is often used in creating hybrids that flower on their own, but are rich in THC.
Growers can then purchase these hybrid seeds and enjoy producing their own buds without worrying too much about flowering light cycles (more on that later).
Hybrids
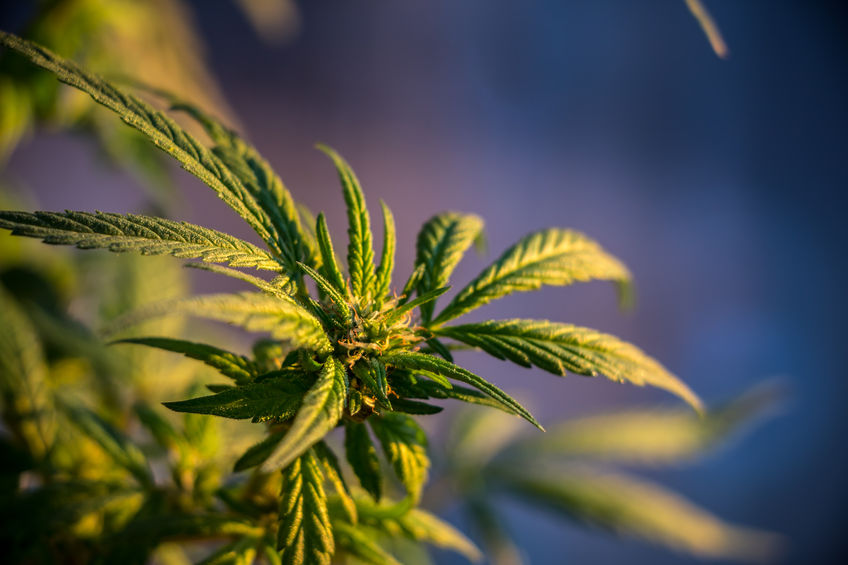

Hybrid cannabis strains are a combination of Cannabis indica, sativa and occasionally ruderalis strains.
Hybrids can happen naturally in the wild, but the ones that we come across in online shops and dispensaries are cultivated on purpose.
When it comes to hybrids, there is no standardization. The plant’s size, smell, taste, potency and flowering depend on the strains used for crossbreeding.
Therefore, the flowering time varies and the plant’s effects range from strain to strain. Hybrids are also a popular choice among breeders and they are usually the most prominent product in online cannabis shops.
There are 3 kinds of hybrid strains:
- Sativa dominant hybrids: Produce a buzzed high, coupled with euphoria and uplifting feeling.
- Indica dominant hybrids: Produce a more body-oriented high with a strong relaxing effect.
- 50/50 hybrids: Provide a balanced high, with mild intoxication.
In between its main strains, cannabis producers have managed to cultivate hundreds of unique strains that each have a purpose on their own.
Quick Break
Wohoo! We went over a lot of information so far and I think it’s time we take a quick break. Watch this video of a baby panda escaping a crib, take a sip of water and continue on when ready.
Chapter 4
Cannabis Products
Now that we know the biology and classification of cannabis strains, let’s move over to the next step—discovering the most popular cannabis products.
Legalization of marijuana paved the way for a wide array of products, all of which have the same goal:
To transport cannabinoids into our bloodstream and provide relief (or a high).
People now use cannabis not just for smoking, but also for creating oils, tinctures, edibles, capsules and other products.
In online shops you will often encounter following products:
- Flowers
- Concentrates
- Edibles
- Tinctures
We’ll first explain each of these and then explore some common consumption methods in the following chapter.
Flowers (Buds)
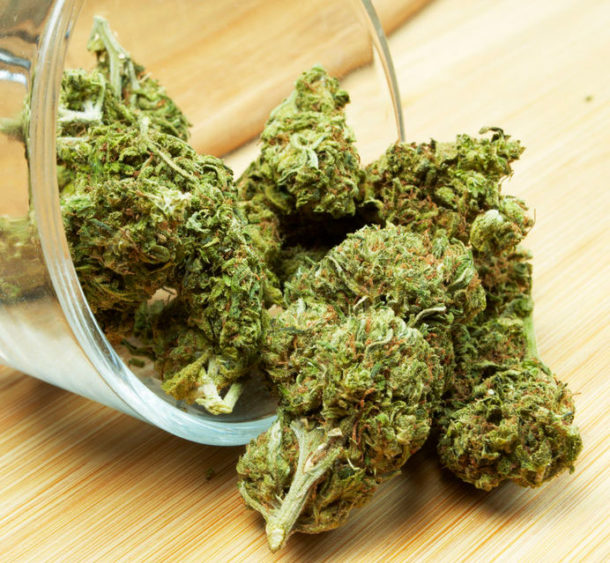

Dried cannabis flowers are, by far, the most popular cannabis product. They are often consumed through joints and bongs, however they can also be decarboxylated and used in edibles.
THC percentages in dried buds vary from strain to strain, but they usually range from 1-20%.
Here applies the same logic from the second chapter: The higher the THC percentage, the stronger the high.
CBD percentages in dried flowers can vary in the same way, however, you will usually encounter CBD levels in areas of 5-15% in CBD dominant strains.
Concentrates
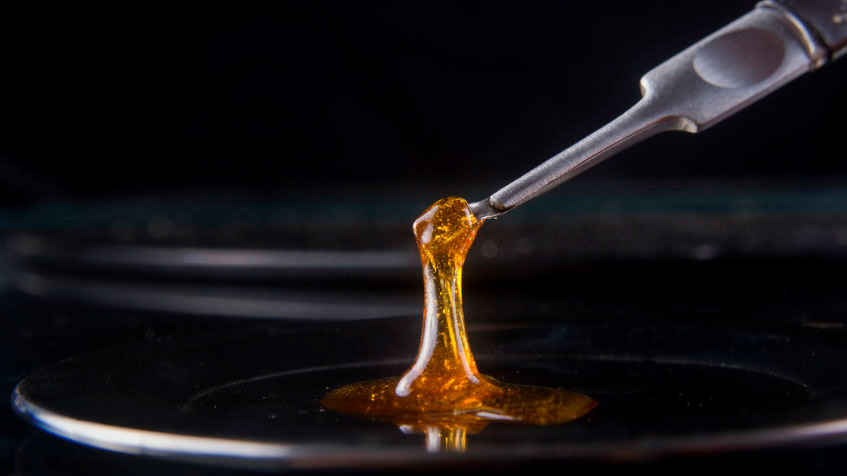

Concentrates are the second most popular cannabis product and they are highly concentrated forms of cannabis, packed with potent cannabinoids.
Concentrates encompass a variety of products:
- Hashish
- Kief
- Moon rocks
- Rosin
- Shatter
- BHO
Concentrates are rich in either THC or CBD (depending on the strain used for extraction) and percentages of cannabinoids tend to stay in the higher range, as much as 80-95%.
Concentrates are produced through extraction: usually, producers would use a dissolvent (like ethanol) to wash trichomes off the flowers.
After filtering, the remaining liquid would be boiled. Once the alcohol evaporates, all you have left is a thick concentrate — rich in whatever cannabinoid profile the flower had.
Concentrates can be vaporized using a special type of vaporizer that supports them, but they are most often consumed by dabbing.
Edibles
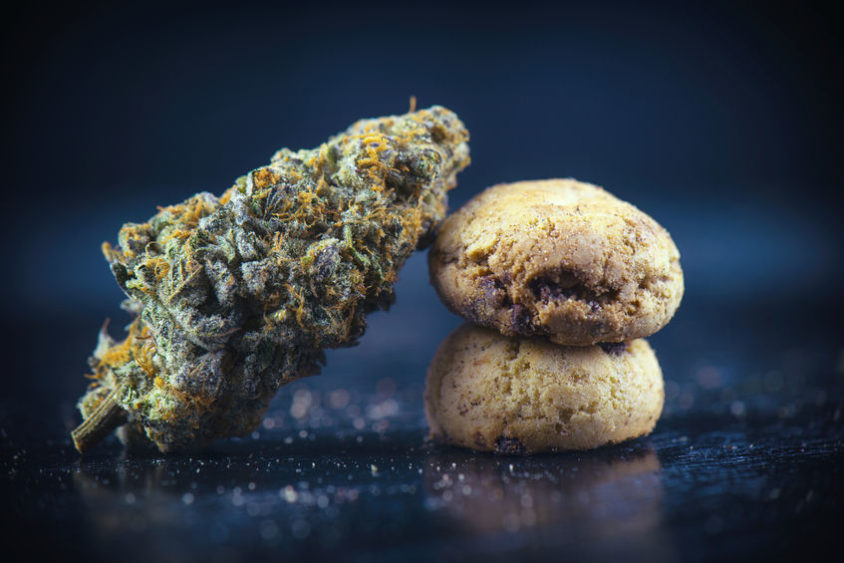

Even though there are producers who make their own commercial edibles, everyone can make them on their own by following these simple cannabis recipes.
Commercial edibles include cannabis chocolates, brownies, bubble gums, lollipops and more.
Cannabinoid percentages within them vary, however, the high from edibles is more potent than when smoking and lasts longer.
Chapter 5
Cannabis Consumption 101
Even though cannabis can be a pretty plant when it’s flowering, you won’t feel any of its effects just by looking at it.
For that reason, it’s important that you become familiar with all the various ways in which you can use it.
Here are the 2 common consumption methods:
- Inhalation
- Smoking
- Vaporization
- Oral consumption
Smoking is usually the first choice for novice users and it is achieved by burning up a cannabis flower and then inhaling the smoke.
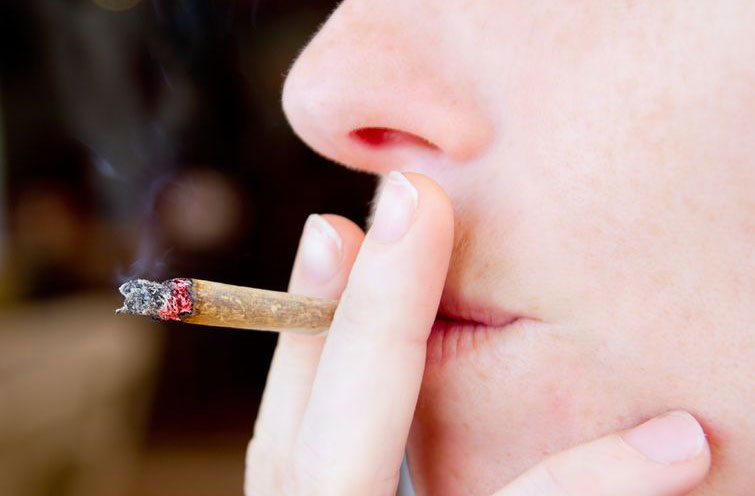

The heat releases cannabinoids, which go into your lungs and into the bloodstream. The high produced by smoking is almost instant and lasts for about two hours, depending on the strain.
Vaporization is a method of inhaling cannabis by heating up a flower or an oil to 315–410 °F using a vaporizer, and then inhaling the gas that is produced.
This is considered less harmful than smoking, due to the lesser amount of produced carbon monoxide and other toxic materials.
Vaporization produces the strongest effects out of all consumption methods and is not recommended for first time users.
Oral consumption is a less common, but still popular, method of consumption. It involves consuming food, drinks, pills and other digestible products.

This consumption method takes several hours to kick in, but the effects are much more potent and longer lasting — the high produced by oral consumption can last up to six hours.
Beginner Smoking Tutorials
One particular area that cannabis beginners find difficult at first is how to get started with smoking marijuana.
Common apparatuses used for smoking are joints and bongs. To learn how to use each of these, just click on the links below and they’ll take you to our tutorials.
These are just 2 basic smoking techniques, but feel free to check out some of our other consumption tutorials, which involve various oral and inhalation methods, as well as vaporization.
Chapter 6
Cannabis Cultivation & Production
Growing cannabis for the purpose of harvesting buds is a complicated process at first, however it’s useful to know the basics.
Once you learn the basics of cannabis cultivation, you may want to try it out on your own as a hobby and see if you can cultivate the next superstar strain.
However, the purpose of this chapter is just to get you familiar with the process.
There are 3 must-know processes that go into growing and producing cannabis:
- Knowing the cultivation requirements
- Following the plant’s development stages
- Harvesting, drying & curing flowers
Cultivation Requirements
Cannabis, like any other plant, needs a certain set of conditions in order to be healthy and produce the highest quality yield.
Licensed producers are following these requirements strictly, as doing so significantly influences the plant’s potency, taste, smell and flowering.
We have 5 points of interest here:
Growth medium
Cannabis can be grown in soil or hydroponically. However, quality is always of the utmost importance.
That means that the soil needs to contain nutrients and a balanced pH level, between 5.9 and 6.5.
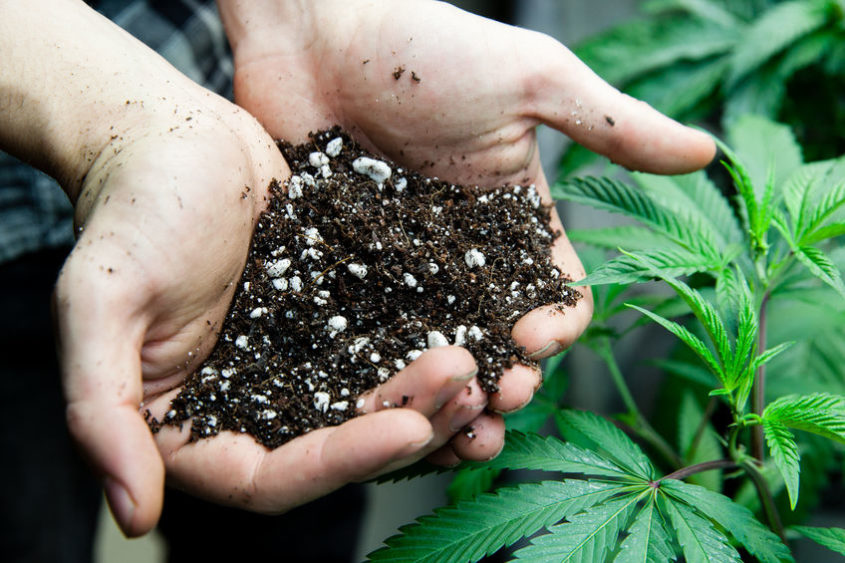

Some examples of good soil for cannabis are Roots Organic and Harvest Moon. Quality cannabis soil is dark, with loose texture and good water retention.
Light
Regardless of whether it’s grown indoors or outdoors, cannabis needs to follow certain day-night light cycles in order to go through its development stages.
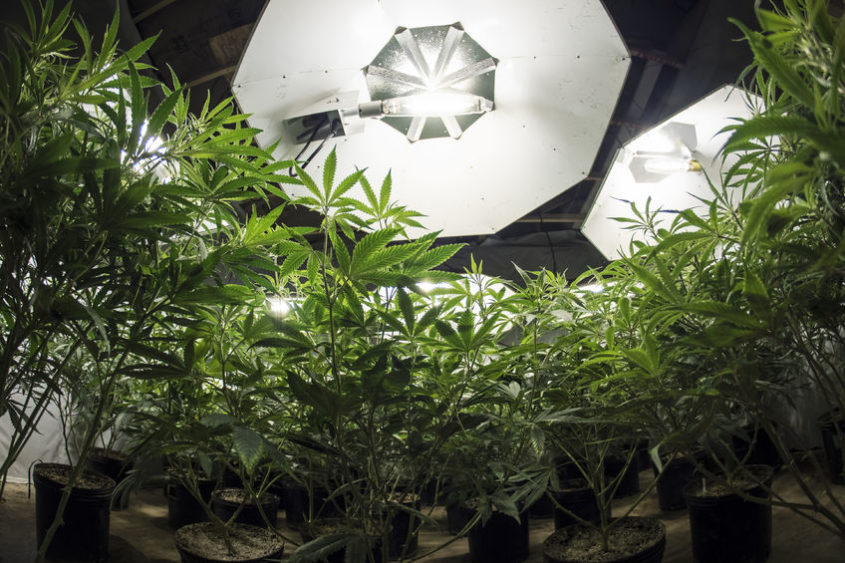

In indoor growing (which is the most common nowadays) plants usually go through a 18-6 cycle, meaning 18 hours of light, 6 hours of darkness.
This light regime involves using different kinds of bulbs, with ranging strength in lumens.
Once the plant matures and start flowering, it is exposed to a 12-12 cycle, which boosts its flower production to the max.
Climate
In order to achieve maximum cannabinoid potency, it’s best to grow cannabis between 24°C and 30°C. Humidity also needs to be controlled through every step of the plant’s development.
Water
It’s important to maintain the soil’s optimum humidity level, so the plant does not dry up. Growers also use pH water to regulate the pH levels in the soil.
Nutrients
Last but not the least, nutrients are strategically administered (preferably through organic fertilizers) once the soil’s own nutrients are depleted.
Expert growers also use a lot of other organic additives, such as rooting hormones, which contain Vitamin B and important acids.
Plant Development Stages
As you know by now, cannabis plants can be either male, female or both. Having in mind that all medicinal and recreational products come from female plants, we will present the plant’s development through an example of a female plant.
However, have in mind that the basic process is the same for both sexes, the only difference being in the plant’s mature/flowering stage.
With that in mind, there are 5 different stages of plant’s development:
- Seed germination
- Seedling stage
- Vegetative stage
- Pre-flowering stage
- Flowering stage
Seed Germination
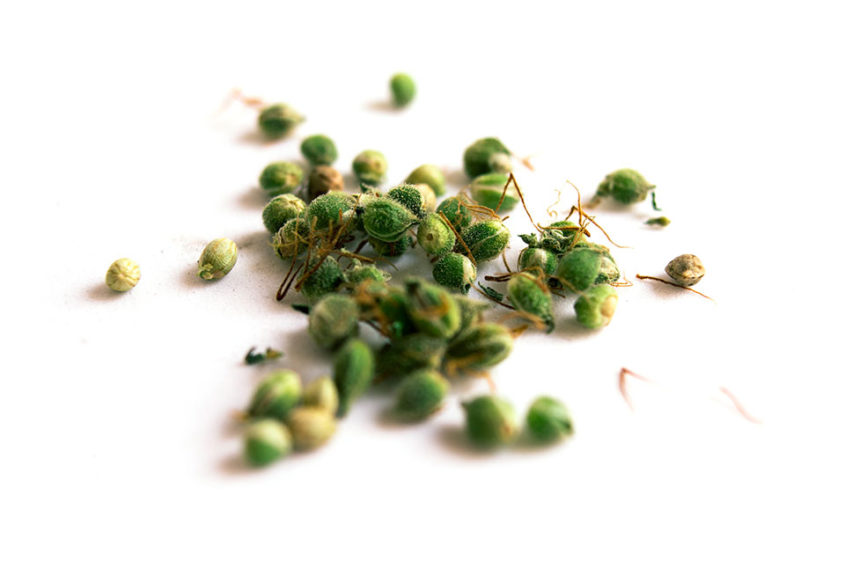

Seed germination is the first process in the plant’s development. Seeds are germinated by soaking them in water infused with Hydrogen Peroxide or between wet paper towels.
After 24 hours of germination, a small, white root pops out of the seeds. This signals to the grower that the plant is ready to be planted in the soil and start its development process.
Seedling Stage
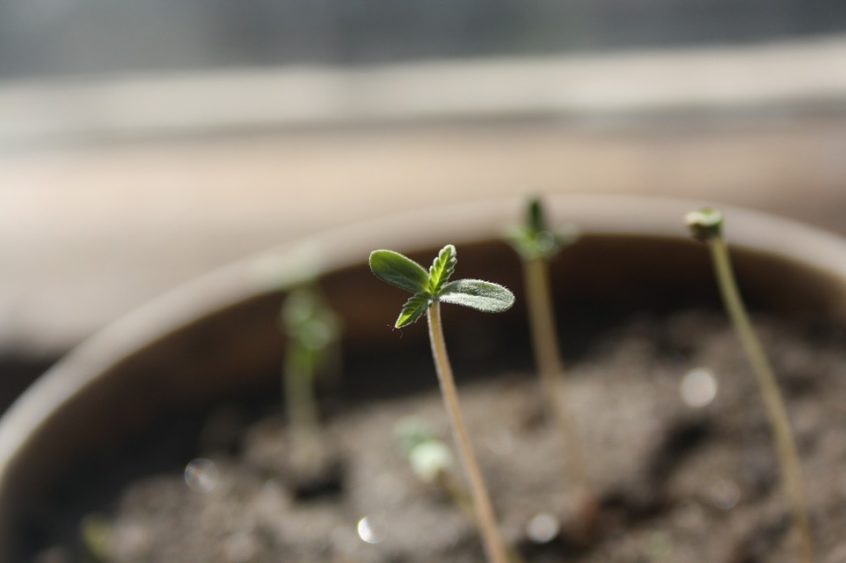

After 2 days of planting the seeds, the seedling stage begins and lasts for 2-4 weeks. During the seedling stage, the root emerges and two baby leaves form — these are called cotyledons, or seed leaves.
In this stage, the plant is extremely fragile and needs special attention in terms of light, water and temperature.
Vegetative Stage
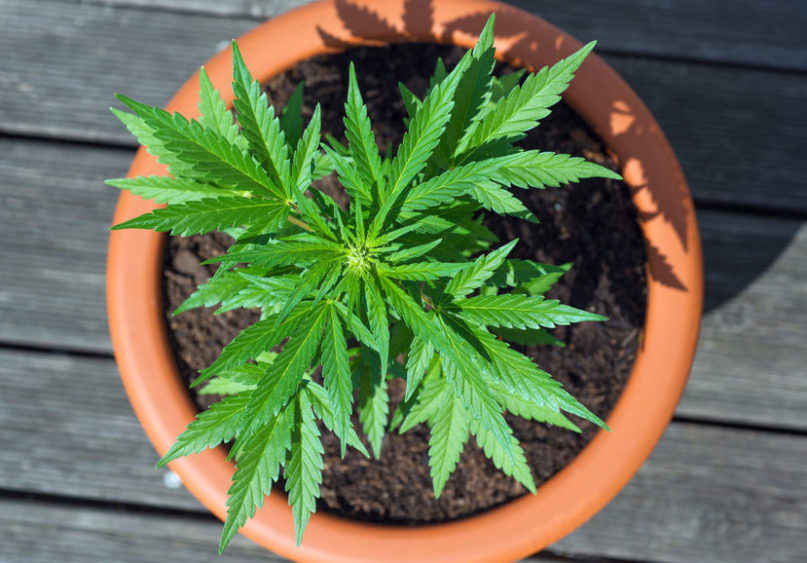

Vegetative stage lasts for 4-8 weeks and is characterized by the plant’s first serious growth in size.
Here is where growers add different nutrients into the soil, which help the plant produce strong roots and nodes.
This is a stage when the plant focuses on creating strong roots, leaves and stems, which will support its flowering in the best possible way.
Pre-flowering Stage
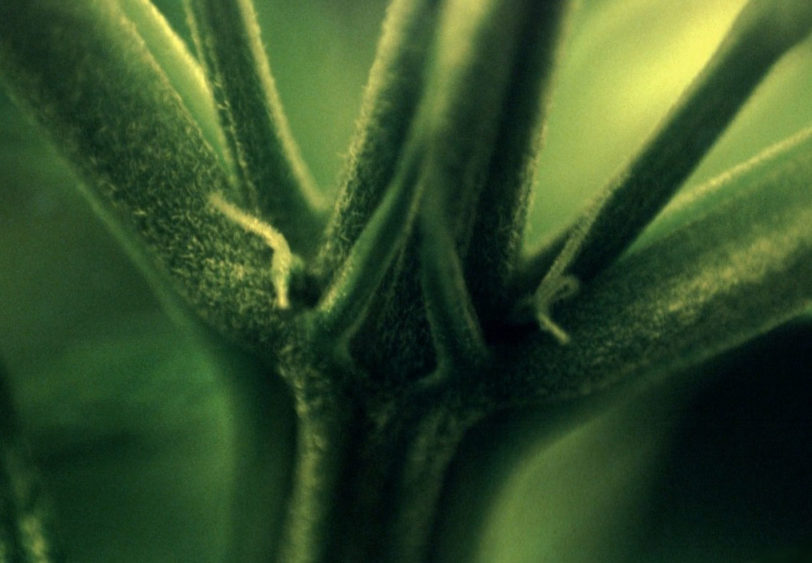

Pre-flowering stage happens around 6-8 weeks after seed germination and in this stage the plant shows its sex for the first time.
If a plant starts growing small hairs (pistils) on its nodes it is a female and if it starts forming small pollen sacks then it’s a male plant. The pre-flowering lasts 1-2 weeks, after which the plant goes into its flowering stage.
Flowering Stage
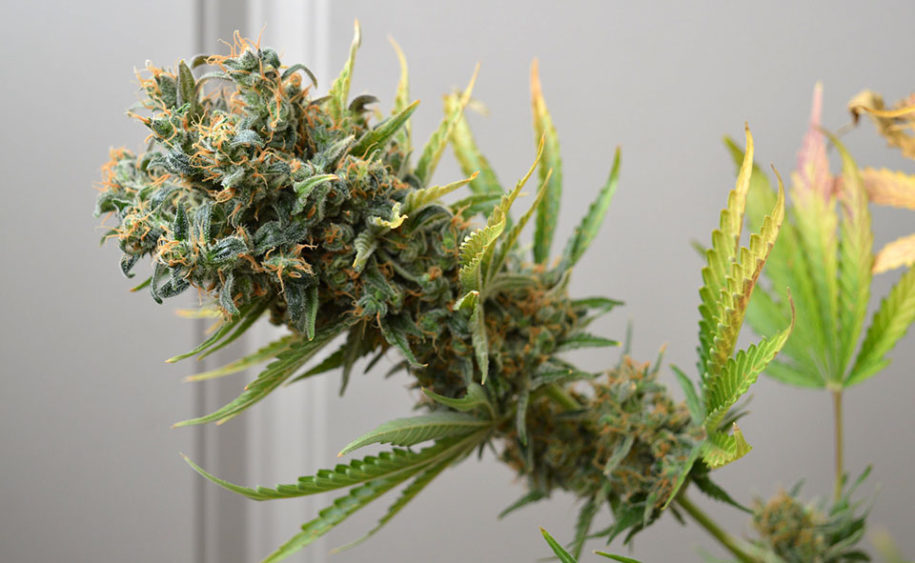

Image source: Cannabis Pictures
Flowering stage is when the plant starts producing flowers, along with trichomes that are rich in THC, CBD and other cannabinoids.
Also, this is when the plant experiences its biggest growth — by the third week of flowering, the plant can be up to 50% bigger than when it started this final stage.
Both the flowers and the plant grow little by little, until the 4th week of flowering, when the plant fully matures and starts committing all of its energy and nutrients to growing flowers.
Cola’s grow and expand until the plant’s 8th week of flowering stage, when the flowers are ready for harvesting, curing and drying.
Fun fact — most cannabis plants can live up to 10-12 years if taken care of properly.
Harvesting, Drying & Curing
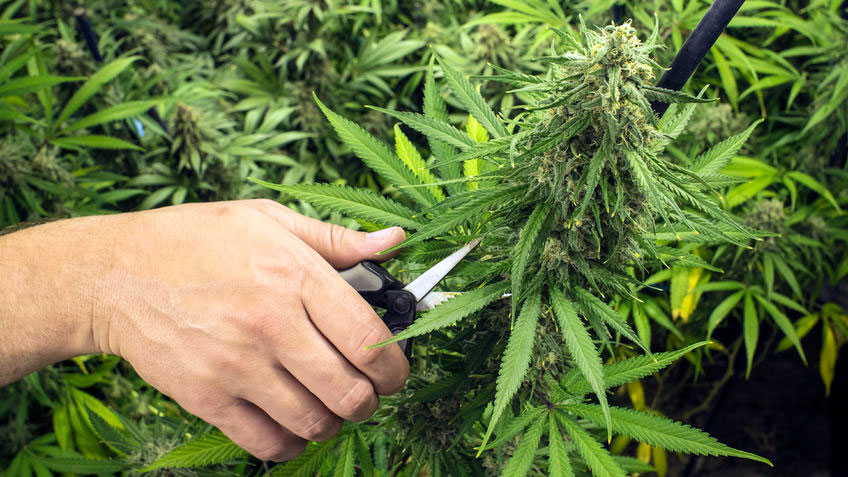

Knowing exactly when to harvest cannabis flowers is really down to grower’s expertise.
The most accurate way of assessing the flower’s maturity is by looking at its trichomes using a magnifying glass.
Once the trichomes start getting cloudy and amberish, the flower is ready for harvesting. Fan leaves are removed and the sugar leaves are separated from the bud and used for creating concentrates (as they also contain trichomes).
Stalks containing flowers (buds) are cut off from the plant and after trimming the bigger leaves, the buds are ready to be dried and cured.
This is essential for providing a smokeable product with high potency and superior flavor.
Drying is done by keeping the buds in a dark place at room temperature, for about 1 week.
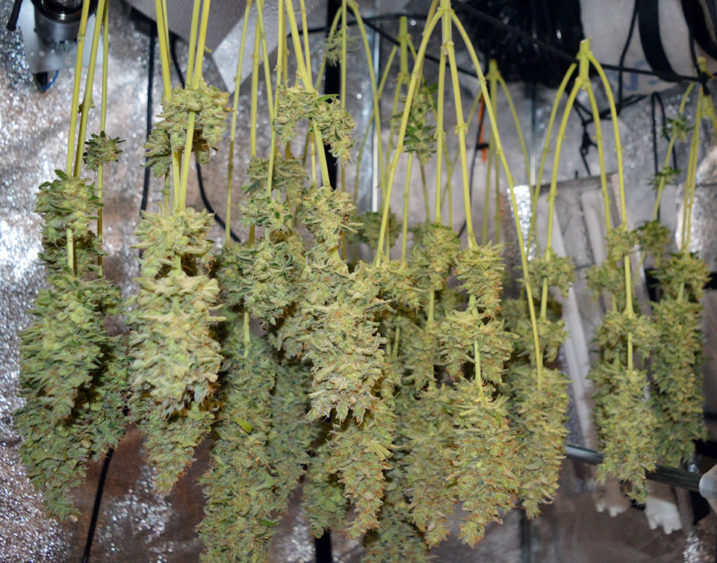

Image source: Cannabis Pictures
Afterwards, the buds need to be cured, which is done by placing them in a sealed jar for 30 days.
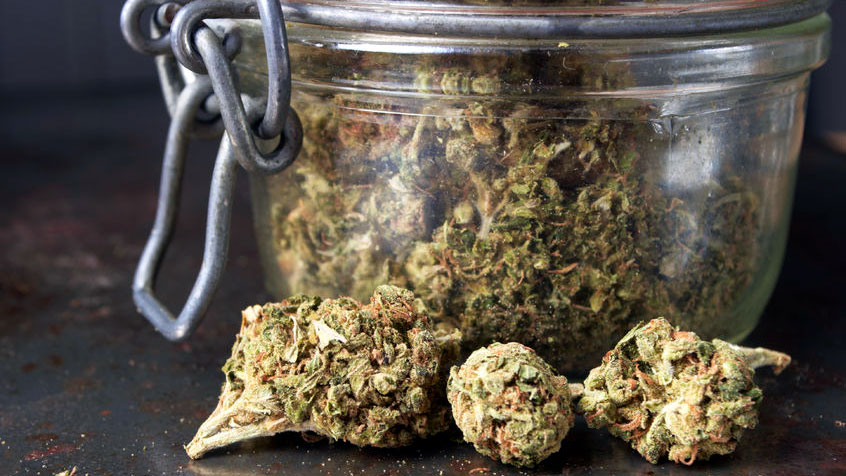

The end goal is for each bud to have around 60% moisture, evenly distributed throughout the bud. That ensures a perfectly crafted product, with the best possible smoking taste and smell.
Properly cured buds can be stored for several years without losing too much potency, however, if you made it this far in this guide, I don’t think you’ll ever test their expiration date.
So, to recap: it can take from 4-6 months for a female cannabis plant to go from a seed to its full flowering stage. Add about 4-6 weeks of drying and curing to that and we come to a total of 7 months for one yield, start to finish.

Cannabis is a plant that shaped entire movements and it’s completely different than anything you’ve ever encountered.
It has the power to heal as well as entertain and it’s been used by humans for millenniums.
As an entity, it’s products can be used in up to 15 different industries and it went from a taboo to a globally accepted herb, constantly being in the limelight of popular culture.
And right now, it’s at your fingertips.













High Country Healing July 27, 2018 at 1:29 pm
Your blog post gives best info about marijuana, Hopefully people would find very useful information from this article.
Luka July 27, 2018 at 1:35 pm
Thanks a lot, we try to do our best!
Ken Stockbridge February 11, 2019 at 12:55 pm
I would like to know if its good to trim roots? If so, whats the best method and when to be done?
Luka February 12, 2019 at 9:20 am
Alex, our resident growing expert says no--if the root is too big you should move it into a bigger pot. :)
Randall Hood March 15, 2019 at 7:25 pm
Hey luka, i am growing hemp and was curious if the drying process was the same if I'm going to use the entire plant as bio mass. Do you leave the flowers on the plant and dry the entire thing ?
Luka March 18, 2019 at 5:12 pm
Hi Randall, as far as I know, you'd use just the stalk and post-extraction flowers for biomass. There's a lot of CBD in flowers, which is what they usually do with them and then use the rest for industrial purposes. I think bio fuel can be made from hemp seed oil. As far as the drying process goes, I think it's completely the same, however, I would do some more research on that. Actually, I tried to dig something up on drying hemp for biomass but there's no content on this topic whatsoever. Might be a good idea for us to cover. :)
Hugh McFadden February 17, 2020 at 11:43 am
Starting out at 58yrs after seeing the light (green)... Loving learning from this newly found site. Thanks, Hugh